Download and view the report offline
Introduction
In 2021, The Legal 500 partnered with Irwin Mitchell to produce our ESG Risk Report. Since then, we’ve seen environmental and social issues dominate corporate agendas, but comparatively, there has been little focus on governance. This is despite the fact that implementing a robust corporate governance plan provides a framework which will maximise protection for the stakeholders’ interests, reduce reputational risks and help companies to gain an advantageous position in the market.
Traditionally, board directors have, almost exclusively, been responsible for governance-related matters; however, as the role of general counsel (GC) evolves, and as the results of our survey suggest, board members are looking to their in-house counsel to pre-empt and reduce governance risks. Further, with many sustainability questions and issues not yet being clearly addressed by regulation, in-house teams are rightly being asked to work with people across their business to put resilient governance and reporting frameworks in place.
We surveyed over 115 in-house lawyers worldwide to gather their insights for how to develop and implement successful and forward-looking governance programmes.
In-House Legal Research Team – GC Magazine
Irwin Mitchell Comment

Although the G in ESG rarely makes the headlines in the same way as environmental and social factors, good governance is fundamental for building trust in and across any organisation, as well as long term sustainability and value.
How businesses operate is increasingly influenced by a wide range of stakeholders including employees, customers, suppliers and communities as well as shareholders and investors. Their priorities and values go far beyond regulatory and legal requirements, and the bottom line. For GCs and in-house teams, this means that the landscape of risks and opportunities that they oversee has changed considerably in recent years, and the pace of change continues to accelerate.
I’d like to thank everyone who contributed to this research for sharing their time and insights with us. We hope you’ll find this report a useful resource for guiding your business in developing and achieving its governance aspirations. But this is just the start of the journey, and we’d love to hear your thoughts on how governance and the role of the GC in progressing this agenda will evolve
from here.’
Hannah Clipston, Director of Strategic Growth, Irwin Mitchell
Foreword
Board members across the world are familiar with the theory of effective governance. It embraces several key aspects, including regulation, compliance, good practice and board ability. Over the past few years, a two-fold evolution has meant the traditional appreciation of governance has moved on from the textbook approach. First, the role of general counsel has undergone significant transformation in the past decade, which has broadened its scope to strategic partner, prompting companies to expect corporate counsel to – among other things – provide advice and strategic guidance on corporate governance and all ESG-related matters.
The second evolution concerns the concept of governance itself. The concept has historically been used to describe transparency and accountability within the corporate sector. As business models have evolved and become more complex, companies have used governance models to enforce ethical corporate behaviours, both internally as well as with external stakeholders.
The past few years have seen a proliferation of statements, proposals and revised codes of corporate governance. While some of these statements reaffirm conventional doctrines and practices, others call for efforts to better align corporate activities with society’s interest in building a more inclusive, equitable, and sustainable economy.
In today’s market, with a customer base that holds expectations that can exceed a business’s legal and regulatory obligations, and is becoming more discerning on where and with whom they do business, ensuring alignment between a business’ purpose and what it does in practice is critical in building trust, both internally and externally.
In-house counsel have a pivotal role to play in the development and implementation of effective governance programmes that will steer the way a business conducts itself and ultimately, its success.
Key factors: In good governance
The research identified three key factors in creating a governance framework that is successful. These issues were repeated by the in-house community, regardless of sector and geography.
Focus on engagement: before creating your framework, spend time on gaining buy-in from all levels of the business including the board, the wider leadership team and team leaders who will be accountable for implementing the framework. Take time to listen to the business about their day-to-day work, challenges, expectations and what works well already. Socialising ideas and changes is important too.
Furthermore, ‘always listen, learn and adapt, because the theory doesn’t always work in practice’.
When developing the framework, keep it simple and use training to ensure that everyone is clear on what the objectives and expectations are and why they are important. You may also consider starting small with some key areas, gaining traction and then growing from there, rather than introducing wide-ranging changes in one go.
‘Make sure you have a progressive plan. Start small and get buy-in from leadership and employees, and then move to bolder actions’.
Create a framework that is specific to your organisation, its goals, strategy and risks as well as the regulations it is bound by. Hiring consultants or carrying out research within your sector will help you to gain insights and ideas which can be adapted into achievable and measurable governance objectives that will resonate within your business.
‘Every organisation is unique. Connect with your organisational requirements to propose a customised governance module that offers a mix of innovation and dynamism without making the stakeholders uncomfortable.’ Or, more succinctly put: ‘don’t copy and paste’.
This report considers each of these factors in more detail and provides practical guidance on how to achieve each of them.
Engagement with your board
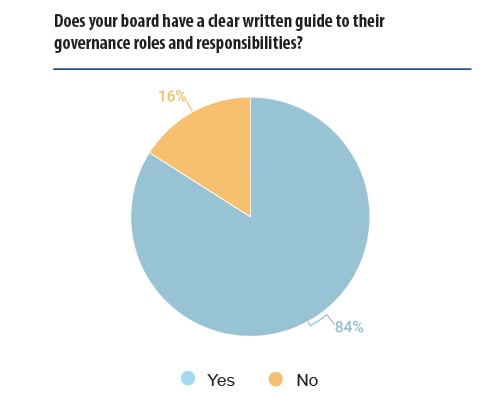
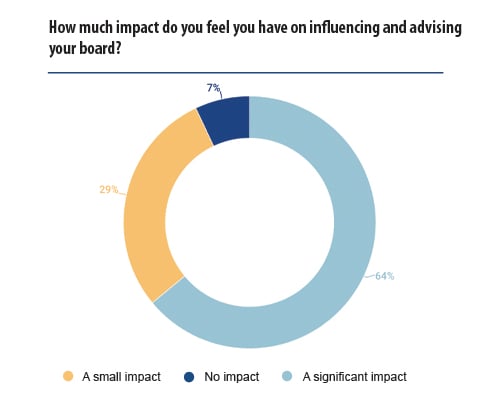
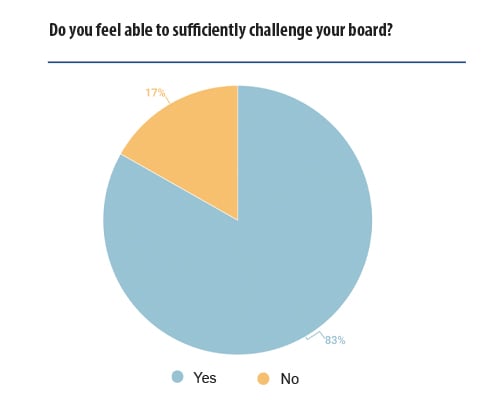
One of the key factors for achieving good governance identified in the survey was the ability for GCs to influence the board, and it is positive that the majority of the respondents felt they could both influence and challenge their board of directors.
Influencing and challenging your board
GCs play a crucial role in advising the board when it comes to risks, compliance and regulatory-related issues. But to be truly effective, GCs need to look beyond their immediate area of expertise. As one GC said to us, ‘we are not only lawyers, we are part of the business. I think my advice to other GCs would be: you have to be part of the board, because first of all, you are part of the business.’
Overall, even though a vast majority of GCs expressed the ability to sufficiently challenge boards of directors, the respondents expressed an interest in having more direct engagement at board level. This would help them to have a better understanding of the business drivers and focus on the ways the legal ecosystem can support them. ‘Our role is to prevent any risks the company faces in its business and projects. Direct access is the best way to influence it’, another interviewee explained.
Advice: How to increase your influence in the boardroom
The advice from our respondents, for those looking to increase their influence in the boardroom can be split into three key areas:
First and foremost you need to be in the boardroom, and once you are there:
- Invest time in winning support from senior advocates
- But always maintain an independent advisor role and don’t shy away from uncomfortable truths
- Don’t be afraid to express your views on non-legal matters
Always keep one step ahead in order to proactively provide training, guidance and advice
- Implement a robust horizon scanning programme to ensure that whatever the future risk might be, they hear it from you first
- Spend time to understand all facets of the business and create training and guidance focused on specific business priorities and risks
- Be crystal clear on what your expectations of the board are
Articulate the value of good governance
- Quantify risks in relation to brand values, reputation and business operations
- Measure and benchmark progress so it can be used to demonstrate competitive advantage to your board
- Ensure your messages are considered constructive rather than obstructive and always frame advice so that it speaks directly to business needs and future growth
Who evaluates the board?
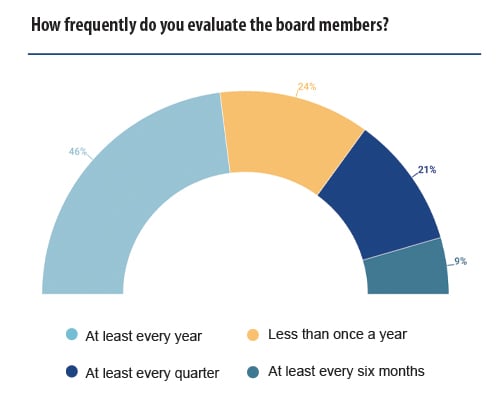
When you have achieved buy-in from your board, or are trying to do so, understanding the evaluation procedure for the board is critical. The ideal scenario is to link good governance, along with other E&S targets, throughout the organisation with reward at a board level. However, that can only occur when there is a clear and transparent board evaluation culture and procedure. Here, we look at how boards are currently evaluated.
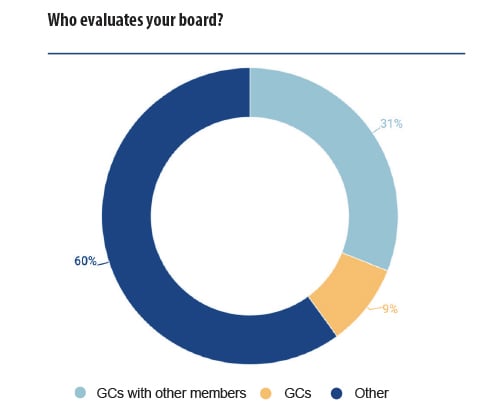
Typically, the board of directors carries out a self-assessment where it evaluates itself, often alongside an external independent group, such as a consultancy or audit firm. Some boards of directors take the view that relying solely on self-assessment may provide either the perception of a conflict of interest or may lead to a biased assessment. Therefore, in these cases, this evaluation is carried out by an external auditor to provide, in the opinion of one respondent, ‘an objective view’ of the status of the company.
As one respondent notes, due to the structure of many companies, members of in-house counsel may be part of developing a governance programme, but they generally do not participate in follow-up assessments of whether compliance has been met. One GC noted: ‘As an employee I do not evaluate the board of directors. The board does a self-assessment regularly with the assistance of an external consultant’. If, however, as some companies have done, they brought in-house counsel onto the board of directors, this would allow GCs to continue their involvement in governance frameworks beyond their initial development.
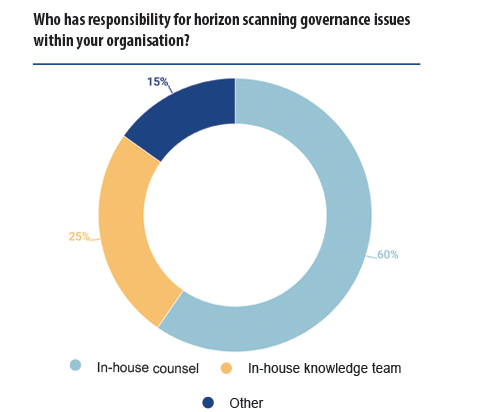
Notably, 60% of respondents noted that GCs did not participate in evaluating the board. Within this cohort, the responses included self-evaluation by the board; evaluation by an internal team not connected to in-house counsel, such as shareholders; and/or evaluation by an external team.
Interestingly, in some cases, even when governance standards had been adopted, some respondents expressed disappointment about a lack of any standards for board members. One respondent said, in response to our question as to who evaluated the board of directors, ‘No-one. Unfortunately’. This shows that while even if good governance policies have been set, that is only the first (and perhaps) easiest step. Without a way to reliably evaluate whether standards have been met, proposed governance programmes will be no more valuable than the paper they’ve been printed on.
The responses by in-house lawyers made clear that they felt linking board performance on good governance to objectives and reward, coupled with an external and independent entity to evaluate performance, provides a valuable incentive for the board to promptly implement governance goals in measurable ways. Unfortunately, this has yet to happen in many organisations and continues to be an area for improvement.
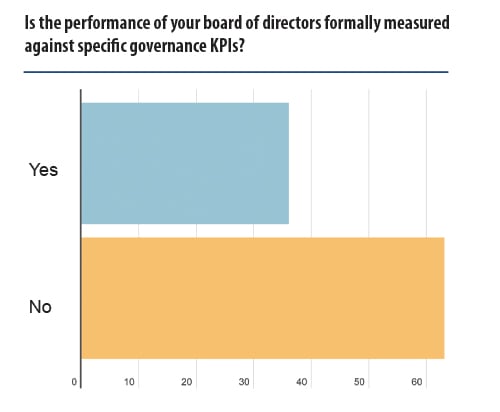
A follow-up survey addressed both measurement of performance of boards and remuneration of directors. The first question’s respondents gave a strong split, with one third noting performance was formally measured against specific governance KPIs.
Some responses noted they implemented the S&P’s DJI ESG scores, while others had developed bespoke policies, with one noting their 2030 agenda consisted of ‘30 cross-company goals that align to outcomes of sustainability, equity and trust’. Others emphasised corporate compliance, gender equity and diversity, while some highlighted a ‘specific focus’ on ‘ethical-related risks’ or a ‘holistic view on enterprise risks’.
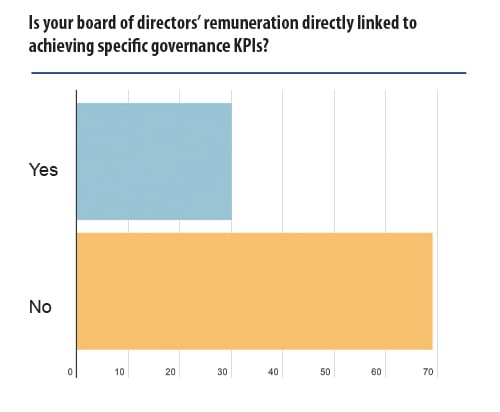
The responses to the second follow-up question track the first, with a little under one third noting that their board of directors had remuneration policies directly linked to achieving specific governance KPIs.
Cross-referencing the two questions, we discovered a full 54% of respondents had neither any formal measurement in place, nor any remuneration to boards of directors directly linked to achieving specific governance KPIs. Only 21% of respondents had both formal measurements in place as well as a form of remuneration in place to boards of directors directly linked to achieving specific governance KPIs.
This demonstrates that there is still a long way to go for boards to be collectively and personally accountable for governance in their organisations. However, it is clear that progress is being made and it will be interesting to evaluate if those who have created a firm link develop a better governance culture and improve business performance as a result.
Diversity in boards
Another key issue that companies are faced with when considering good governance is the diversity of their board, including gender, ethnicity and diversity of thought among others. While this is often something in-house advisors may struggle to influence it does bear consideration, including when looking at how to influence your board and what issues may have differing levels of importance to them. Here, we look at the thoughts of those surveyed on the diversity of their own boards.
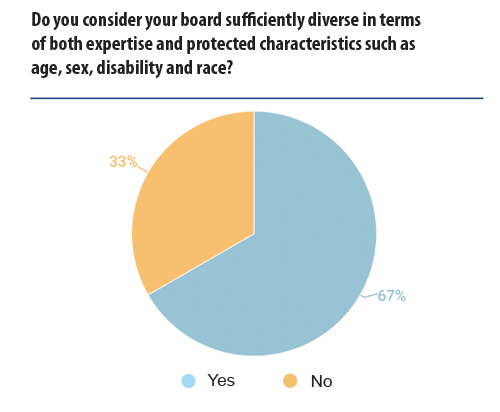
The statistical data provides a positive sign regarding diversity on boards of directors, with two thirds believing their boards of directors to be sufficiently diverse. This reflects a strong focus in recent years on board diversity, with the associated improvement in governance it is felt this can bring. It was, however, noticeable that the feedback from GCs who responded with ‘No’ painted a general picture of frustration from in-house counsel that their board of directors were generally older, white men, and what steps had been taken to improve diversity regarding gender were, in the words of one respondent, ‘minimum and limited’.
However, while some expressed frustration at failures to diversify boards of directors, others expressed optimism towards future improvements: ‘We have taken actions, including raising the non-diversity issue with the local board and explaining to them how this lack of diversity will be perceived’. It should be taken as a positive that improvements have been made and that action continues to create more balanced and diverse boards which are essential for tackling increasingly complex commercial issues, often requiring innovative and creative solutions.
Irwin Mitchell Comment
‘Increasing diversity at board level helps to create more inclusive and collective governance, and strengthens an organisation’s ability to respond to and anticipate change in ever-evolving markets and client bases. Greater diversity has been shown to bring about improved productivity and performance, a more responsive approach to client needs and increased innovation and creativity through a sense of belonging and the power of diverse thought. Therefore, a diverse range of board members brings with it a valuable range of perspectives and experiences to decision-making and problem-solving.
You also can’t underestimate the power of senior role models, particularly at board level, for under-represented groups and the impact this has on an organisation’s culture. While change on this doesn’t happen overnight, more can be done to recognise where there is a lack of diversity at board level and in wider decision-making groups and to seek out more diverse views to inform decision-making. Board members can act now and challenge views presented to them to ensure that diverse views have been taken into account in shaping proposals and policies prior to approval, while work takes place to increase the overall diversity of the board and the talent pipeline within an organisation’.
Charlotte Delaney, Diversity and Inclusion Manager, Irwin Mitchell
Irwin Mitchell Comment
‘Looking to the future, businesses are having to think more and more about how to generate innovation in order to respond to increasingly complex customer needs. Within Irwin Mitchell, we want to ensure that our products and services evolve so we are constantly exceeding client expectations. We know this is dependent upon attracting and retaining diverse talent and future leaders so we can benefit from different perspectives and experiences at all levels across our business. This starts with a commitment to widening access and increasing social mobility and by participating in initiatives like our new mentoring programme with City University, access to work experience with PRIME and increasing our apprenticeship offerings, we provide opportunities for students who might not otherwise have considered a career within the legal sector.’
Satinder Bains, Partner and Chair of Irwin Mitchell’s Social Mobility Colleague Network, IM Aspiring
Keep it simple
Ensuring your governance framework is simple and well understood is key to its success. Complex structures lead to a lack of understanding and engagement. This section looks at some of the challenges to embedding a good governance structure, and with winning buy-in from the business’ people at the top of the list, the importance of a simple, well understood and articulated plan cannot be overstated.
Challenges to embedding good governance
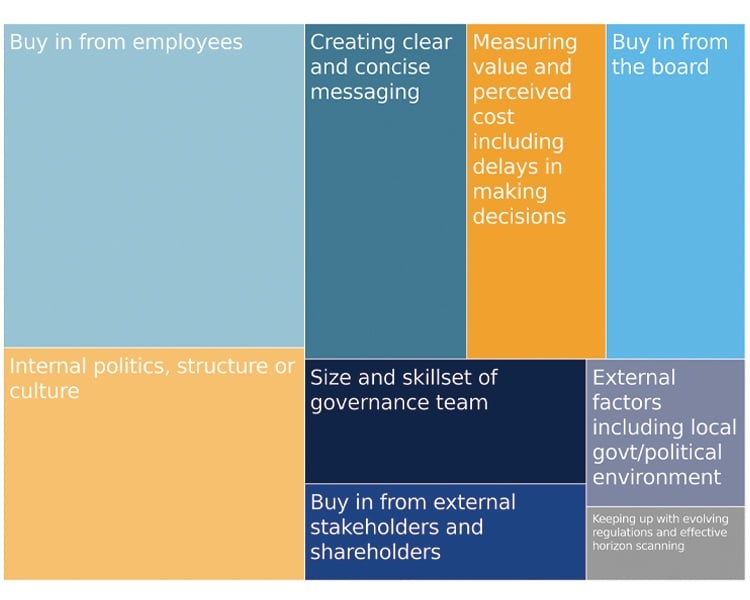
We asked about the main challenges to achieving good governance in an organisation, and while some cited difficulties caused by external factors such as local culture and politics, the majority of responses related to internal factors that GCs can actually influence.
Employee buy-in is considered the main challenge to achieving good governance, and this is noted as particularly tricky in organisations with high staff turnover, where employees are located over multiple sites and jurisdictions, and when people are already time-poor. But clear and concise messaging will go a long way to garnering buy-in. In addition, small steps can help bed in the framework, creating a simple starting point which can then be built on.
As one GC we spoke to pointed out: ‘The biggest difficulty is communicating clearly and in a manner that cuts through the noise of so many other regulatory, reputational and business demands on the attention of all stakeholders, including, not least, employees’.
Similarly, boards and other stakeholders will be more inclined to support governance issues if they have clarity on the costs of taking or not taking certain actions.
Formulating a simple framework which includes measurable principles provides valuable data which can be used to the advantage of the business. 75% of those surveyed said they use governance data and achievements in their marketing to employees and new hires, as well as customers.
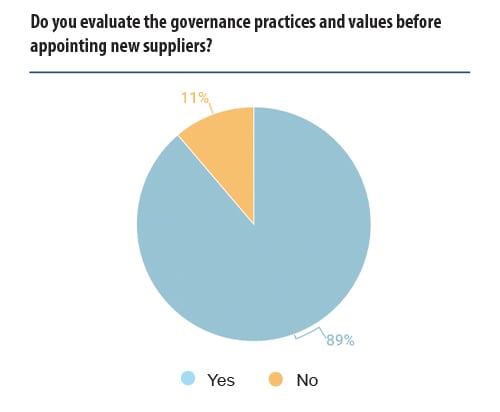
At a time when GCs are increasingly looking for ESG as part of their own supplier procurement process, having readily available and clear metrics on ESG compliance, including governance, is becoming a must-have for any business who wishes to grow, recruit and attract investment.
Irwin Mitchell Comment
‘A robust governance framework is critical to our Responsible Business strategy. As well as ensuring that we set sufficiently challenging KPIs and objectives around our work, we engage external partners and participate in a number of benchmarks and accreditations to measure our progress and ensure that we continue to make an impact. We report on our performance in our annual Responsible Business report.’
Kate Fergusson, Head of Responsible Business, Irwin Mitchell
Make it specific
A key factor in success was making the framework specific to your organisation. This will necessitate in-house counsel understanding the needs and issues within their business and prioritising their governance objectives accordingly, which will then naturally flow into the framework for your organisation.
This section considers the priorities and aspirations from those surveyed, to provide support when considering some of the aspects you may wish to examine while looking at your own specific governance framework.
Governance aspirations
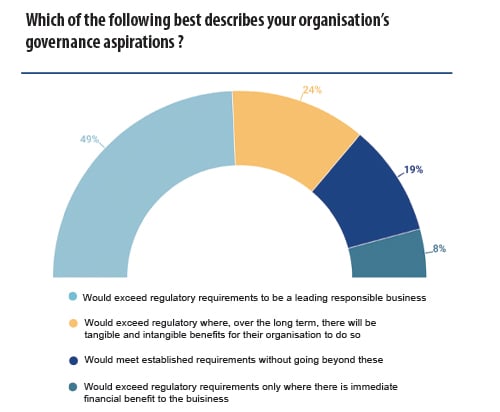
In our study, we found that most companies’ governance aspirations go beyond regulatory requirements. 48.7% of those interviewed stated that they would exceed regulatory requirements to be a leading responsible business because, simply, it is the right thing to do, rather than for commercial
gain. A further 23.5% say they would exceed regulatory requirements where, over the long term, there will be tangible and intangible benefits for their organisation to do so.
These figures demonstrate that for many, governance has moved on from being seen as a compliance exercise to a more strategic framework built to support sustainable business growth and impact.
19.3% of those surveyed would meet the established regulatory requirements without going beyond these, and the remaining 8.4% would exceed regulatory requirements only where there is an immediate financial benefit to the business, such as on cost savings.
Irwin Mitchell Comment
‘The direction of regulation and of client, colleague and community expectations around Responsible Business are clear and accelerating. Today’s aspirations and “nice to haves” will soon become tomorrow’s bare minimums. And changes of this scale in business take time to implement effectively. So a significant factor for the long term sustainability of all businesses is anticipating successfully the direction in which change in the business ecosystem is happening – and not just looking at today’s position (as you will fail to meet future needs if you do) – and then starting the change process proactively in that direction so that the needed changes are completed in the business in line with or even ahead of, rather than behind, the competition.’
Bruce Macmillan, GC, Irwin Mitchell
Understanding your priorities
priorities for the next 12 months
For the majority of respondents, the main focus for the year ahead is on their governance policies, frameworks and programmes. For some, it is about putting these into place while others are looking to refresh and update. Improving accountability and compliance also scored highly.
Looking at specific types of risk, unsurprisingly ESG tops the list, and drilling down further it is environmental issues that are highest on the agenda. This reflects the general trend in society and from stakeholders to ensure these issues are considered and understood, and appropriate governance procedures put in place to manage the risks.
As to cybersecurity and data privacy, respondents pointed out how organisations benefit from a comprehensive, integrated and centralised strategy for achieving data privacy compliance. Data sharing, they say, should have stricter controls and policies, which implies either current legislation is not being complied with or does not go far enough. Organisations should develop more solid data security compliance methods to track personal data in accordance with legal standards.
Irwin Mitchell Comment
‘We often see that organisations don’t have a complete picture of all the data sharing happening either from an intra-group perspective or with third parties. This is particularly the case with increased globalisation – there is often data export which is overlooked. For example there can be line management in groups done by managers in other group companies and other countries. IT and tech contracts often have an international aspect somewhere in the supply chain. Since the compliant export of personal data is a hot topic at the moment for the ICO and the European regulators it is important to understand what data sharing and export is happening and to ensure that it is compliant. Things are complicated by the fact that the data export rules and standard export contracts have changed recently. The old approach of signing EU standard contractual clauses and forgetting about them doesn’t work anymore. The issue will be further magnified once the UK data protection reform happens. We don’t yet have sight of the draft legislation after the Data Protection and Digital Information Bill was scrapped but we understand that it is still on the cards.’
Joanne Bone, Partner – Commercial and Data Protection
Prioritising your framework
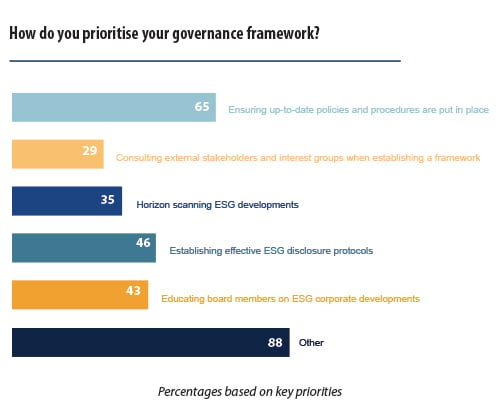
In terms of priorities, over 60% of GCs stressed the importance of having adequately up-to-date policies and procedures in place. This is a key starting point for any governance framework but it must be specific – companies should not adopt policies for the sake of it where they are not necessary or adding value. Over 40% consider the most pressing matter as the establishment of effective governance disclosure protocols and educating board members on governance developments. Less than half of the people interviewed see the necessity of consulting external stakeholders and interest groups when establishing a governance framework (29.41%) as a number one priority.
Nonetheless, it is interesting to note that under the category ‘other’, the majority indicated that their priority lies in organising training for all stakeholders to better achieve good governance and create a sustainable change. When it comes to taking the ultimate responsibility for achieving good governance, the general feedback is that this is a collective task, however,
the board of directors and key managerial personnel have the last word. The board’s purpose is to support corporate performance and establishing clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and appropriate measures for evaluating against those KPIs. Linking that success (or failure) to reward helps focus the board on the importance of good governance.
This reflects the contents of this very report: that board engagement, simple policies which employees can understand and are trained on, aligned with a framework for for your business, are how you can achieve good governance success.
Irwin Mitchell Comment
‘Creating a Culture of Compliance, as we are doing, needs to have a clear metrication of what is right – directionally and in terms of what a material improvement or deterioration looks like; clearly and openly spelt out to leaders and team members – we use a Balanced Scorecard with Key and Leading Performance Indicators; and then their needs to be a clear, explicit and adhered to approach that makes good or poor compliance a material reward and promotion issue.’
Bruce Macmillan, GC, Irwin Mitchell
Looking to the future
Having established and embedded a good governance framework, the work of an in-house lawyer is not complete. Good governance practice continually evolves. This report has already flagged the importance of independent monitoring of compliance and performance against the background of the governance framework set. However, from a commercial perspective, the focus of a business will shift to reflect new trends and demands from stakeholders, customers and employees.
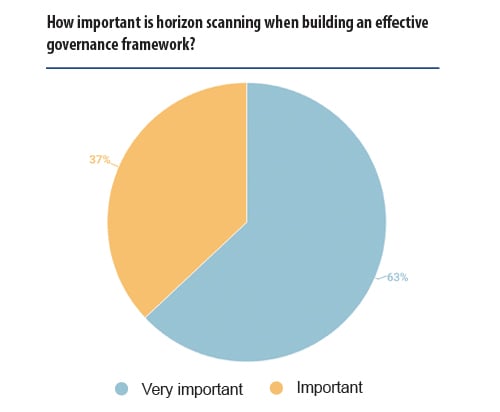
Keeping your governance policies and procedures up to date requires a strong emphasis on horizon scanning, together with regularly revisiting your materiality assessment to understand the key issues for your stakeholders and which will impact your business and governance framework.
Like the captain of a ship, in-house counsel need to be able to identify ‘hidden icebergs’ and thorough horizon scanning will detect future disruption along with new opportunities to build into responsible business plans which will positively impact their business and society. Effective horizon scanning also provides decision-makers with the time to plan their response, and clear communication with external partners ensures those in the supply chain have the opportunity to ‘stay ahead of the game’.
As well as relying on monitoring services and updates from external experts including law firms, auditors, regulators and the government etc, the GCs surveyed take advantage of networking events, training and digital forums such as LinkedIn groups to ensure they are keeping up to speed with what is on the horizon.
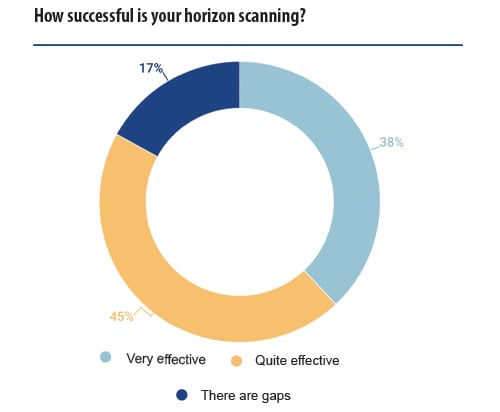
The majority replied that the horizon scanning in place is effective in identifying governance issues before they arise. However, gaps persist. Under the gap section, interviewees expressed a willingness to have more resources allocated within the in-house legal team. Until then, working alongside your legal advisors and other sources of updates should be a priority to ensure your governance framework remains fit for purpose.
The pace and scale of societal, economic and environmental challenges facing us means we need to generate innovation and creativity within our organisations to quickly devise and implement solutions. This will require diversity of thought and openness to collaboration across our own business and the wider economy.
By leading the focus on effective governance against measurable KPIs which are understood and supported, GCs can be at the forefront of this challenge, making a difference to not only their organisations, but to society as a whole.
Conclusion and practical tips
Establishing a successful governance framework relies on many different things but its importance to a business should always be remembered. The G in ESG is often overlooked, but for a business to be successful it should be a core part of its focus, from the board to employee. The role of the in-house lawyer in achieving that can look daunting, but by focusing on getting the right engagement, keeping your plans simple and being specific to your organisation, you can achieve success.
In the column on the right, we have set out a checklist from the research to help you assess where you are on your governance journey, and what the next steps are for you and your organisation.
Checklist: For ensuring good governance
Communication
- Are your governance policies available and easy to find for employees and external stakeholders?
- Are your policies written in a way that means everyone is clear on what’s expected in terms of their individual and collective duties and behaviours, and why?
- Do you have a training and communications programme in place to regularly remind people about new and existing governance matters? And for new employees as part of their induction?
Compliance
- Do you undertake scheduled and/or unannounced audits and checks on employees and suppliers?
- Are your procurement documents and standard contracts regularly reviewed and updated to incorporate evolving governance requirements and KPIs?
- Do you have a robust horizon scanning system/process in place to ensure your policies reflect new and forthcoming changes?
People and culture
- Do you (as a GC or more widely as an organisation) have a sufficiently resourced and proactive team with responsibility for creating, implementing, reviewing and measuring your governance programme?
- Does the board ‘walk the talk’? If not, do you have at least one senior leader to be your ambassador?
- Is your board evaluated and rewarded based on successful governance compliance?